.png?width=820&height=547&name=Blog%20Featured%20Image%20(3).png)
If your organization leverages the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud, you have probably encountered the Shared Responsibility Model. This framework is distributed by AWS to delineate security and compliance responsibilities between themselves as the cloud provider and their customers as cloud users.
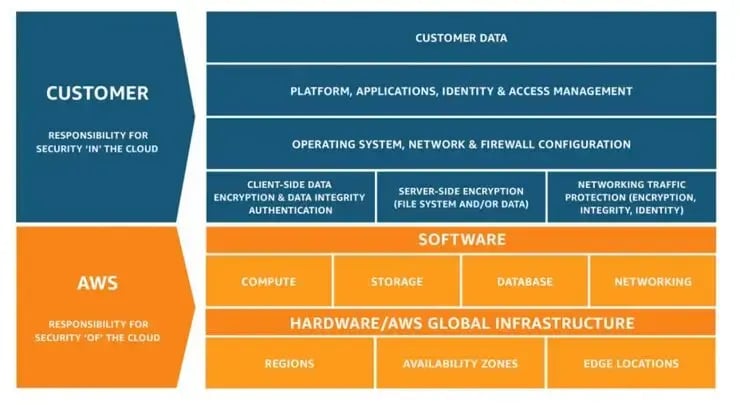
Figure 1. The AWS Shared Responsibility Model
As depicted above, AWS is responsible for the security “of” the cloud, meaning they protect the infrastructure on which cloud services run, while its customers are responsible for the security “in” the cloud, including encryption, network configuration, access management, and customer data. As the customer, your responsibility is determined by the AWS Cloud services that you use. For example, services categorized as Infrastructure as a Service (such as Amazon EC2) require the customer to perform all of the necessary security configuration and management tasks whereas for abstracted services (such as Amazon S3) the customer is required to manage data, classify assets, and apply the appropriate permissions while AWS operates the infrastructure layer, operating system, and platforms.
While all of the above controls are important, there are three reasons why securing customer data is highly important:
- First, appropriately securing customer data can prevent compliance violations and save millions of dollars in possible fines and remediation costs.
- Secondly, data security measures simultaneously prevent loss of trust in situations where current end users could face damages from ransomware and malware.
- Finally, securing end user data signals to prospective end users that you prioritize the safety of their data and actively take steps to protect it from risk.
Beyond the reasons to secure end user data outlined above, consider the following: under the Shared Responsibility Model, AWS clearly communicates that it is the customer’s (read as “your”) responsibility, as the steward of end users’ data, to validate the security of the data they (read as “you”) ingest and hold within AWS storage.
Securing Your (and Your Customers’) Data
Modern organizations ingest data from various sources, including customers, partners, acquisitions of new assets, and the public internet. Without proactive protection, there is no way to ensure that this data does not contain malware, including ransomware, that could result in a data breach or another form of cyberattack.
While malware protection is just one component of true data security, it is still a critical tool to avoid the threat of malware ingestion and prevent any accompanying consequences.
When selecting and implementing a malware protection solution, there are a number of important factors to consider:
- Scope and Coverage: The solution should scan all of your data for malware, no matter where it resides. For example, malware could be ingested into Amazon EFS as well as Amazon S3. Both cases can result in a costly data breach.
- Accuracy: The use of multiple, distinct industry-vetted malware scanning engines decreases the likelihood of false positive and false negative verdicts. The difference between a false negative and true positive could be millions of dollars in remediation costs and irreparable damage to your reputation.
- Bandwidth: Automated quarantining, bucket detection, and other features such as malware detonation reduces the amount of time spent monitoring and maintaining the solution, which can free up resources for revenue driving activities and other critical security tasks.
Cloud Storage Security’s (CSS) malware protection solution is an easy-to-configure and highly effective way to scan all data ingested and kept in AWS storage for malware, including ransomware. In fifteen minutes or less, customers can deploy and configure a solution that addresses the threat of malware and helps avoid the consequences of a data breach.
The Consequences of Inaction
Malware ingestion can lead to data breaches which result in a number of consequences, including:
- Monetary Loss: The average cost of a data breach in 2024 has risen to $4.88M, according to IBM, and an average ransomware victim’s shares underperform the NASDAQ by 12%.
- Data Loss: When data is exfiltrated during a ransomware attack, 75% of organizations say that full recovery took longer than 100 days. In the same study, only 3% of organizations could recover in less than 50 days. Considering the time it takes to first discover malware in your data, this timeline could be significantly longer.
- Loss of Trust: More than half (53%)1 of organizations suffered damage to their brand and reputation after a ransomware infection.
Implementing malware protection across AWS storage is a low risk, high reward measure of prevention against the consequences of malware in your data.
Get started with a fully-featured 30-day free trial of CSS’s antimalware solution today in AWS Marketplace. In doing so, you can generate a detailed picture of your current data security posture and make a plan to protect your data as it grows with your business.
Looking for something tailored to your application? Contact a malware protection SME today.
About Cloud Storage Security
Cloud Storage Security (CSS) protects data in the cloud so that businesses can move forward freely and fearlessly. Its robust malware detection and data loss prevention solutions are born from a singular focus on, and dedication to, securing the world’s data, everywhere. Serving a diverse clientele spanning commercial, regulated, and public sector organizations worldwide, CSS solves security and compliance challenges by identifying and eliminating threats, while reducing risk and human error. CSS’s modern, cloud-native solutions are streamlined and flexibly designed to seamlessly integrate into a wide range of use cases and workflows, while complementing and bolstering existing infrastructure and security frameworks. CSS holds certifications including SOC2, AWS Public Sector Partner with an AWS Qualified Software offering, AWS Security competency, and AWS Authority to Operate.
1Source: Freed, Anthony M. “How Do Ransomware Attacks Impact Victim Organizations’ Stock?” Cybereason, 2022.

%20(3)-1.png?quality=high&width=1900&height=1250&name=CSS%20-%20Blog%20(Featured%20Images)%20(3)-1.png)
%20(1).png?width=2000&height=1125&name=CSS%20-%20Blog%20(Featured%20Images)%20(1).png)




